Timing Differences Between Compiling .java Code Files and Executing .class Bytecode Files
- September 28, 2020
- 9367 Unique Views
- 3 min read
Java developers are familiar with the notion that the foundation of Java is "write once, run anywhere." That is, the same Java code will run on all the primary operating systems and hardware platforms. As I noted in my earlier post Why Java, C, and Python Are Today’s Most Utilized Programming Languages, Python comes somewhat close to this (though in my experience what works on Linux may not work out-of-the-box on Windows or Mac), and of course C/C++ require immense adaptation of the software in order for it to work on different operating systems and hardware platforms.
The way Java accomplishes this is through the compilation of Java source code into bytecode, which is what the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) actually executes. Java bytecode is somewhat similar to the Assembly Language utilized by languages like C. Bytecode is a low level instruction set that the JVM executes in order to enact the processing created by the developer with their Java (or any other JVM language) program.
Comparing Java Code and Java Bytecode
Here is a very simple Java program named SumNumbers.java that adds some numbers to come up with a sum, then prints the sum:
public class SumNumbers {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// compute 1 million by addition
int x = 1;
int sumx = 0;
int count = 1000000;
for(count = 0; count < 1000000; count = count + 1)
sumx = sumx + 1;
System.out.println("The total sum is " + sumx);
}
}
We're going to count to 1 Million by adding 1 to 0 a million times. A very simple program.
So, what is happening when this program is run? First, the Java code is compiled into bytecode. In essence, the javac command is run to compile the Java source into Java bytecode, then the bytecode is executed using the JVM.
The performance timing of this is interesting (for reference, I'm running OpenJDK 11 on a fairly old 64-bit Debian Linux system). If I time this javac command:
time javac SumNumbers.java
I get this result:
real 0m0.762s user 0m1.432s sys 0m0.042s
These Linux timings can be a bit confusing. The real time is the total amount of time "from the start to the finish of the call." The user time appears to include the time I spent pressing the "Enter" key and the time that was taken for the result to be displayed on my console. The sys time is the amount of CPU time that was spent in Kernel mode. From these descriptions, I think the real time is what developers will be most interested in, when we're thinking about cloud applications. We don't have a developer press "Enter" every time a customer accesses our application.
The Bytecode
In executing this javac command, we asked the Java compiler to read our input SumNumbers.java file and convert into Java bytecode. If our Java source code is valid, the compiler produces a binary bytecode file named SumNumbers.class.
So, what's in SumNumbers.class? We can see this by executing the following command:
javap -c SumNumbers
Here's what we see:
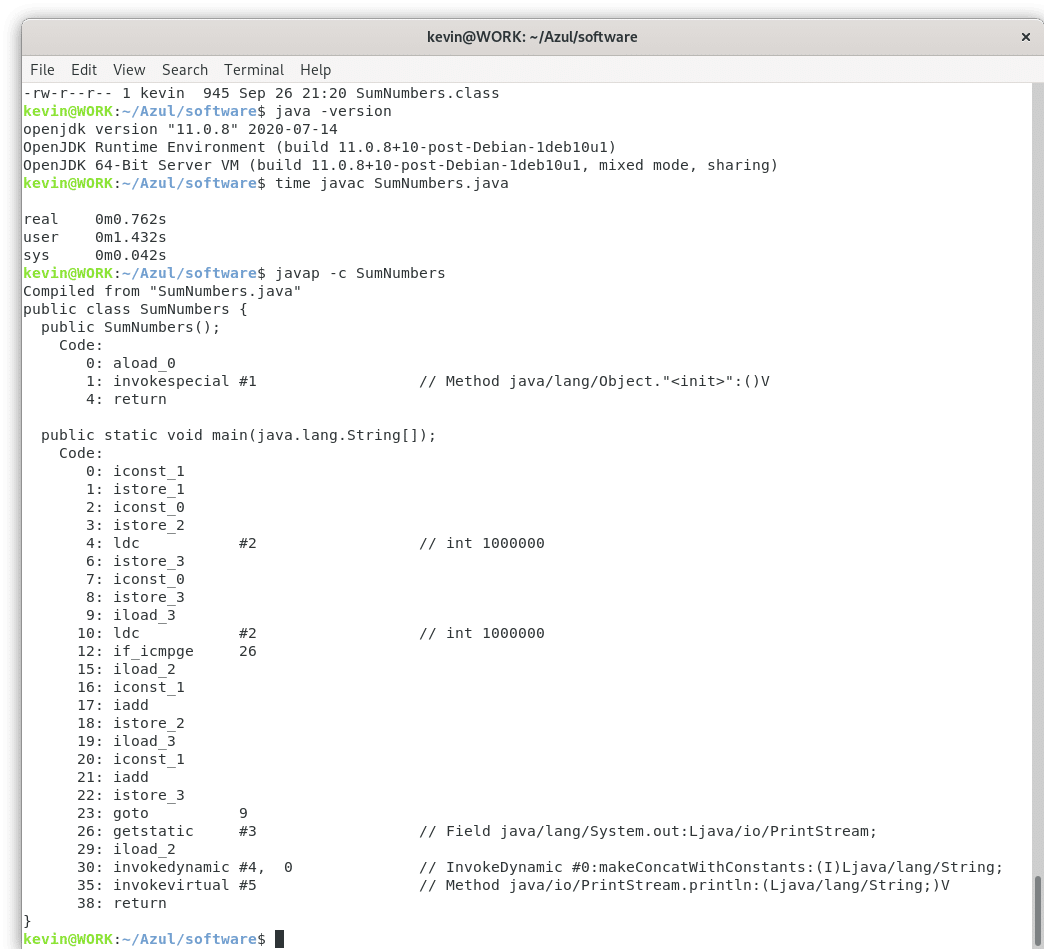
As a matter of fact, though, understanding how Java bytecode works is critical if you are developing high-performance low-latency applications. It's actually possible to edit Java bytecode in order to improve performance. That is, your compiler produced a good first version of Java bytecode, but you have some ideas about how to further optimize the bytecode to increase the performance of your application.
Directly Running Java Bytecode
We can run the Java bytecode that javac produced using the following command:
java SumNumbers
When the java command sees no file extension, it looks for a file that ends with the extension .class; so that command runs the SumNumbers.class bytecode file. Here's the timing we see from doing that on my Linux system:
time java SumNumbers
The total sum is 1000000 real 0m0.088s user 0m0.098s sys 0m0.017s
So, we see that the time to execute the bytecode for this simple program is a small fraction of the time to compile it using javac.
Non-Java JVM Languages
Of course, there are many non-Java JVM languages, like Scala, Clojure, JPython. What type of bytecode do they produce compared with the javac compiler? And how efficient is the bytecode they produce?
I'll look into this in subsequent posts.
Don’t Forget to Share This Post!




Comments (1)
Johannes Boneschanscher
5 years agoThank you for your article, please note however that your interpretation of the cryptic output of https://linux.die.net/man/1/time is incorrect, please refer to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/556405/what-do-real-user-and-sys-mean-in-the-output-of-time1 which explains it in all its glory. Basically it boils down to real time being the time between start and finish (wall clock time) including off-cpu time like waiting for things like user input, disk or network, in contrast to the second and third lines: User and System time are the sum of each child proces or thread being active on the CPU, so thanks to hyperthreading or multicore systems (which is quite common given that even many smartphones have been for years), can be higher than realtime. This might even happen to Java applications that are not multithreaded, but Java itself might do multithreaded Garbage Collection and other background tasks.