CodeRabbit Tutorial for Java Developers
- July 28, 2025
- 12823 Unique Views
- 4 min read
- 1. Code Quality Analysis
- 2. Security Vulnerability Detection
- 3. Performance Optimization Suggestions
- 4. Design Pattern Recognition
CodeRabbit is an AI-powered code review tool that integrates seamlessly with your Git workflow to provide intelligent, automated code reviews.
For Java developers, CodeRabbit offers specialized analysis that understands Java syntax, best practices, and common patterns.
Getting Started
Prerequisites
- A GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps, or Bitbucket repository.
- Java project with standard structure (Maven or Gradle).
- Admin access to your repository.
Setup Process
- Install CodeRabbit
- Visit CodeRabbit.ai.
- Sign up using your credentials, while noting that CodeRabbit is free for OSS, supports GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps, and Bitbucket.
- Grant necessary permissions to your repositories.
- Repository Configuration
- Select the Java repositories you want CodeRabbit to review.
- CodeRabbit automatically detects Java projects and configures appropriate rules.
- Initial Setup Verification
- Create a test pull request with a simple Java change.
- Verify CodeRabbit comments appear within minutes.
Core Features for Java Development
1. Code Quality Analysis
CodeRabbit analyzes your Java code for:
Style and Formatting
// CodeRabbit will suggest improvements for:
public class DemoApplication{ // Missing space before {
private String userName;
public void setUserName(String userName){ // Parameter naming
this.userName = userName;
}
}
For example, when you ask CodeRabbit to check the style above, you'll get a response comparable to this:
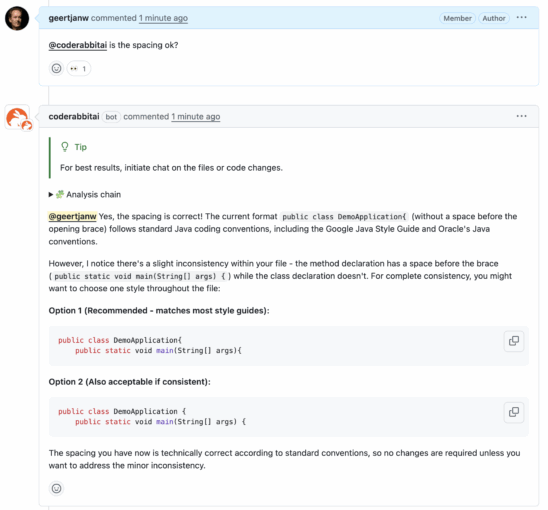
Best Practices
- Proper exception handling
- Resource management (try-with-resources)
- Null safety checks
- Performance optimizations
2. Security Vulnerability Detection
CodeRabbit identifies common Java security issues:
// CodeRabbit will flag potential security risks:
public void unsafeMethod(String userInput) {
// SQL injection vulnerability
String query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '" + userInput + "'";
// Potential XSS vulnerability
response.getWriter().println(userInput);
}
The above is analyzed in several ways, including this, by CodeRabbit:
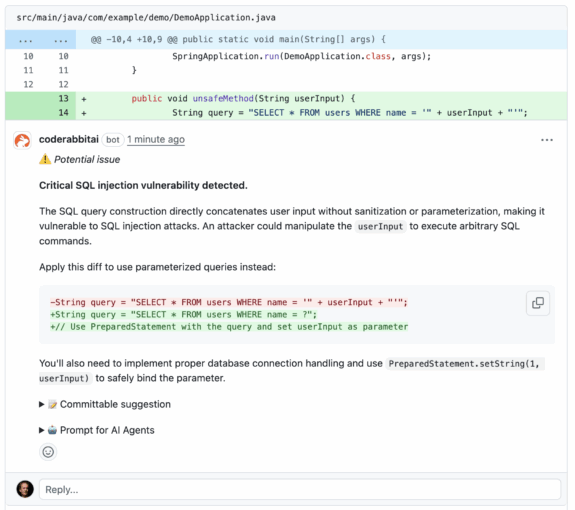
3. Performance Optimization Suggestions
// CodeRabbit suggests improvements:
// Original code
List<String> items = new ArrayList<>();
for (User user : users) {
items.add(user.getName());
}
// CodeRabbit might suggest:
List<String> items = users.stream()
.map(User::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
4. Design Pattern Recognition
CodeRabbit understands common Java patterns and suggests improvements:
// Suggests Singleton pattern improvements
public class DatabaseConnection {
private static DatabaseConnection instance;
// CodeRabbit might suggest thread-safe implementation
public static synchronized DatabaseConnection getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new DatabaseConnection();
}
return instance;
}
}
Working with CodeRabbit Reviews
Understanding Review Comments
CodeRabbit provides three types of feedback:
- Suggestions: Improvements for code quality
- Issues: Potential bugs or problems
- Nitpicks: Minor style or convention issues
Responding to Reviews
Accepting Suggestions
- Click "Apply suggestion" for auto-fixable issues
- CodeRabbit can automatically commit simple fixes
Discussing Feedback
- Reply to comments to provide context
- Use
@coderabbitaito ask follow-up questions in the code review comments - Example:
@coderabbitai Why is this approach better for performance?
Resolving Comments
- Address the feedback in your code
- CodeRabbit automatically detects resolved issues in subsequent commits
Java-Specific Configuration
Custom Rules Setup
Create a .coderabbit.yaml file in your repository root:
reviews:
auto_review:
enabled: true
path_filters:
include:
- "src/**/*.java"
- "pom.xml"
exclude:
- "target/**"
rules:
- security_issues
- bugs
- code_quality
- best_practices
Maven/Gradle Integration
CodeRabbit automatically understands your build configuration:
- Analyzes
pom.xmlorbuild.gradlefor dependencies - Suggests dependency updates
- Identifies unused dependencies
- Checks for security vulnerabilities in dependencies
Advanced Features
1. Custom Prompts
Ask CodeRabbit specific questions about your Java code:
@coderabbitai Can you suggest a more efficient way to implement this caching mechanism?
2. Architectural Reviews
CodeRabbit can analyze larger structural changes:
@coderabbitai Please review the overall architecture of this new service layer
3. Testing Suggestions
CodeRabbit helps improve your test coverage:
@Test
public void testUserCreation() {
User user = new User("John");
assertEquals("John", user.getName());
}
// CodeRabbit might suggest:
// - Additional edge case tests
// - Mock object usage
// - Test naming improvements
Best Practices
1. Preparing Your Code for Review
Before Creating a PR:
- Run local tests and static analysis
- Follow your team's coding standards
- Write meaningful commit messages
- Keep PRs focused and reasonably sized
2. Maximizing CodeRabbit's Effectiveness
Provide Context:
- Write descriptive PR descriptions
- Include relevant issue numbers
- Explain complex business logic in comments
Iterative Improvement:
- Address CodeRabbit feedback promptly
- Use follow-up commits for fixes
- Learn from repeated suggestions
3. Team Collaboration
Code Review Workflow:
- Developer creates PR
- CodeRabbit provides an initial review
- Team members add a human perspective
- Address all feedback before merging
Common Java Patterns CodeRabbit Recognizes
1. Spring Framework
// CodeRabbit understands Spring annotations and suggests improvements
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService; // Might suggest constructor injection
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
// CodeRabbit checks for proper error handling
return ResponseEntity.ok(userService.findById(id));
}
}
2. JPA/Hibernate
// CodeRabbit provides database-related suggestions
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String email; // Might suggest unique constraint
// CodeRabbit checks for proper equals/hashCode implementation
}
3. Stream API Usage
// CodeRabbit optimizes stream operations
List<String> result = users.stream()
.filter(user -> user.getAge() > 18)
.map(User::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList()); // Might suggest toUnmodifiableList()
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Review Not Triggering
- Check repository permissions
- Verify CodeRabbit is installed on the repository
- Ensure PR meets minimum criteria (not draft, has changes)
2. False Positives
- Use
@coderabbitai ignoreto dismiss incorrect suggestions - Provide feedback to improve future reviews
- Add explanatory comments for complex logic
3. Performance Issues
- Large PRs may take longer to review
- Consider splitting large changes into smaller PRs
- Use path filters to exclude generated files
Integration with Development Tools
IDE Integration
- CodeRabbit works with any IDE through Git
- Comments appear directly in your Git provider's interface
- No additional IDE plugins required
CI/CD Integration
- CodeRabbit reviews happen automatically on PR creation
- Can be configured to block merges until issues are resolved
- Integrates with status checks
Measuring Success
Key Metrics to Track
- Reduction in post-merge bugs
- Faster code review cycles
- Improved code quality scores
- Team learning and knowledge sharing
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly review CodeRabbit's suggestions
- Update the configuration based on team needs
- Collect team feedback on review quality
Conclusion
CodeRabbit significantly enhances the Java development workflow by providing instant, intelligent code reviews. By understanding its capabilities and following these best practices, your team can enhance code quality, identify issues early, and expedite development cycles.
Remember that CodeRabbit is a tool to augment, not replace, human code review. The combination of AI-powered analysis and human expertise creates the most effective code review process.
Next Steps
- Set up CodeRabbit on a small Java project
- Experiment with different configuration options
- Gradually roll out to larger projects
- Collect team feedback and iterate on your process
- Explore advanced features as your team becomes comfortable with the basics
For more detailed documentation and updates, visit the CodeRabbit documentation.
Don’t Forget to Share This Post!









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first.