Dynamic watermarking on the JVM
- July 09, 2024
- 2 min read
Displaying images on your website makes for an interesting problem: on one side, you want to make them publicly available; on the other, you want to protect them against undue use. The age-long method to achieve it is watermarking:
A digital watermark is a kind of marker covertly embedded in a noise-tolerant signal such as audio, video or image data. It is typically used to identify ownership of the copyright of such signal. "Watermarking" is the process of hiding digital information in a carrier signal; the hidden information should, but does not need to, contain a relation to the carrier signal. Digital watermarks may be used to verify the authenticity or integrity of the carrier signal or to show the identity of its owners. It is prominently used for tracing copyright infringements and for banknote authentication.
The watermark can be visible to act as a deterrent to people stealing the image; alternatively, you can use it to prove its origin after it has been stolen.
However, if there are too many images on a site, it can be a burden to watermark them beforehand. It can be much simpler to watermark them dynamically. I searched for an existing JVM library dedicated to watermarking but surprisingly found nothing. We can achieve that in a Jakarata EE-based web app with the Java 2D API and a simple Filter.
The Java 2D API has been part of the JDK since 1.0, and it shows.
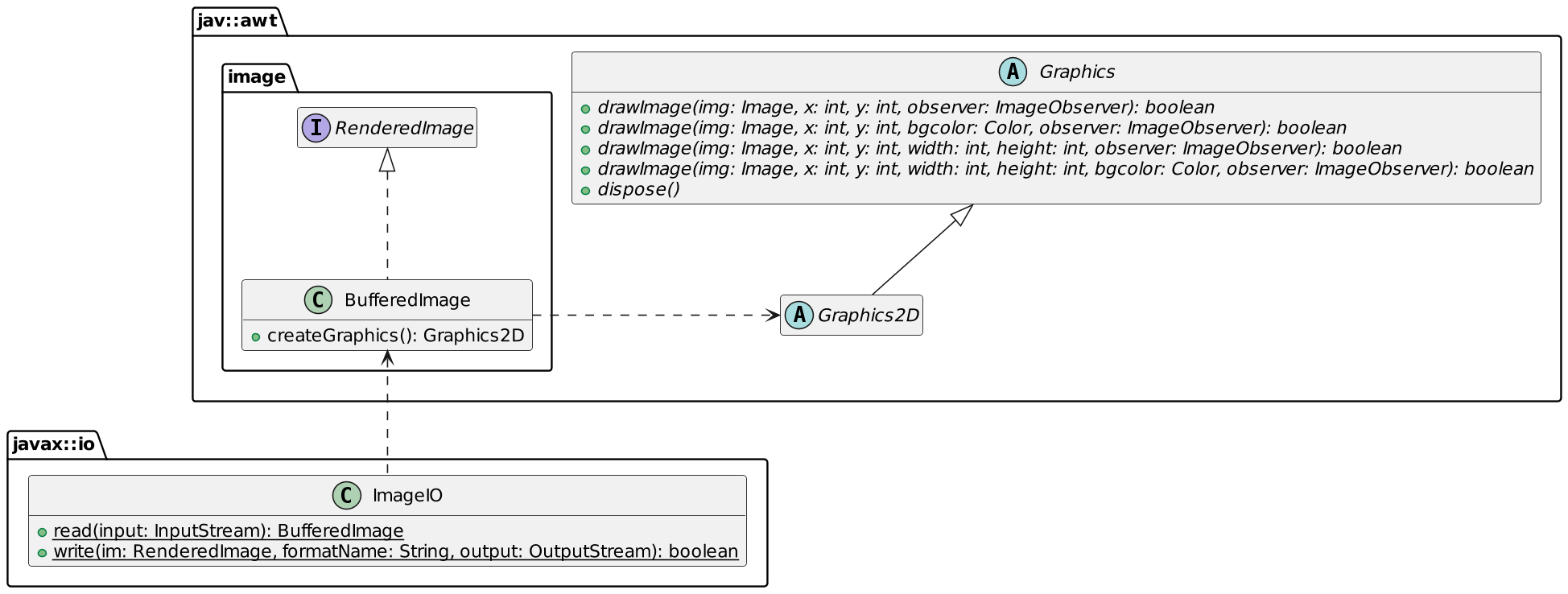
It translates into the following code:
private fun watermark(imageFilename: String): BufferedImage? {
val watermark = ImageIO.read(ClassPathResource("/static/$imageFilename").inputStream) ?: return null //1
val watermarker = ImageIO.read(ClassPathResource("/static/apache-apisix.png").inputStream) //2
watermark.createGraphics().apply { //3
drawImage(watermarker, 20, 20, 300, 300, null) //4
dispose() //5
}
return watermark
}
- Get the original image
- Get the watermarking image
- Get the canvas of the original image
- Draw the watermark. I was too lazy to make it partially transparent
- Release system resources associated with this object
Other stacks may have dedicated libraries, such as photon-rs for Rust and WebAssembly. With this in place, we can move to the web part. As mentioned above, we need a Filter.
class WatermarkFilter : Filter {
override fun doFilter(request: ServletRequest, response: ServletResponse, chain: FilterChain) {
val req = request as HttpServletRequest
val imageFilename = req.servletPath.split("/").last() //1
val watermarked = watermark(imageFilename) //2
response.outputStream.use {
ImageIO.write(watermarked, "jpeg", it) //3
}
}
}
- Get the image filename
- Watermark the image
- Write the image in the response output stream
I explained how to watermark images on a Java stack in this post. I did the watermark manually because I didn't find any existing library. Next week, I'll show a no-code approach based on infrastructure components.
To go further:
Originally published at A Java Geek on June 30th, 2024
State of Java 2026 Webinar
Wednesday, 18 February Azul’s Simon Ritter and Frank Delporte will break down trends across Java adoption, cloud costs, licensing, DevOps productivity, and AI in production.
Register Here!
- July 09, 2024
- 2 min read










Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first.